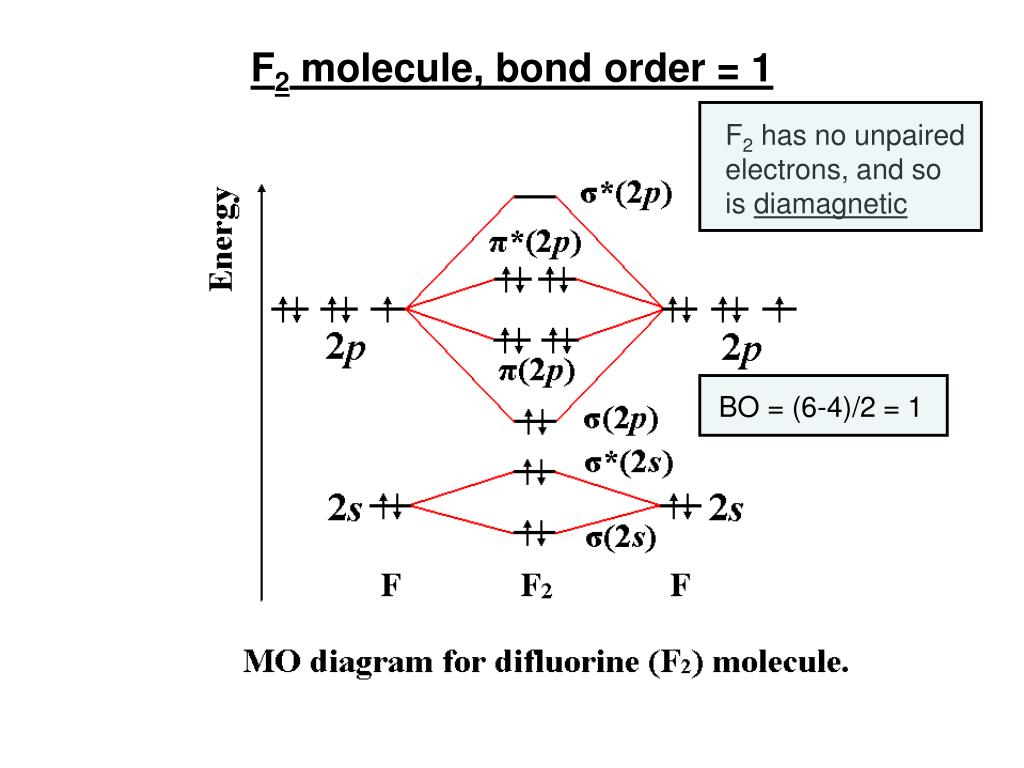
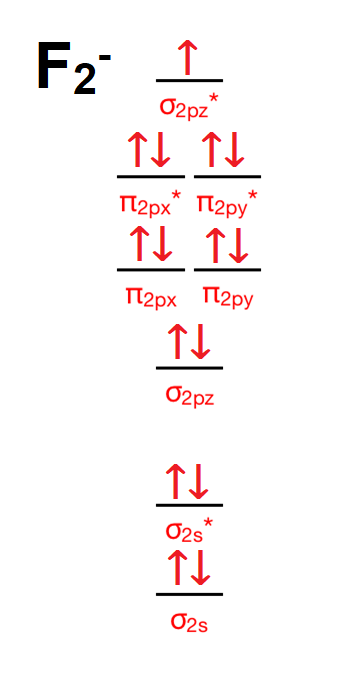
39 f2 molecular orbital diagram
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ... This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2
For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————...

F2 molecular orbital diagram
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading. 0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d... Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Solve Study Textbooks. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Chemistry >> Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure >> Molecular Orbital Theory >> 37. Draw molecular orbital ...
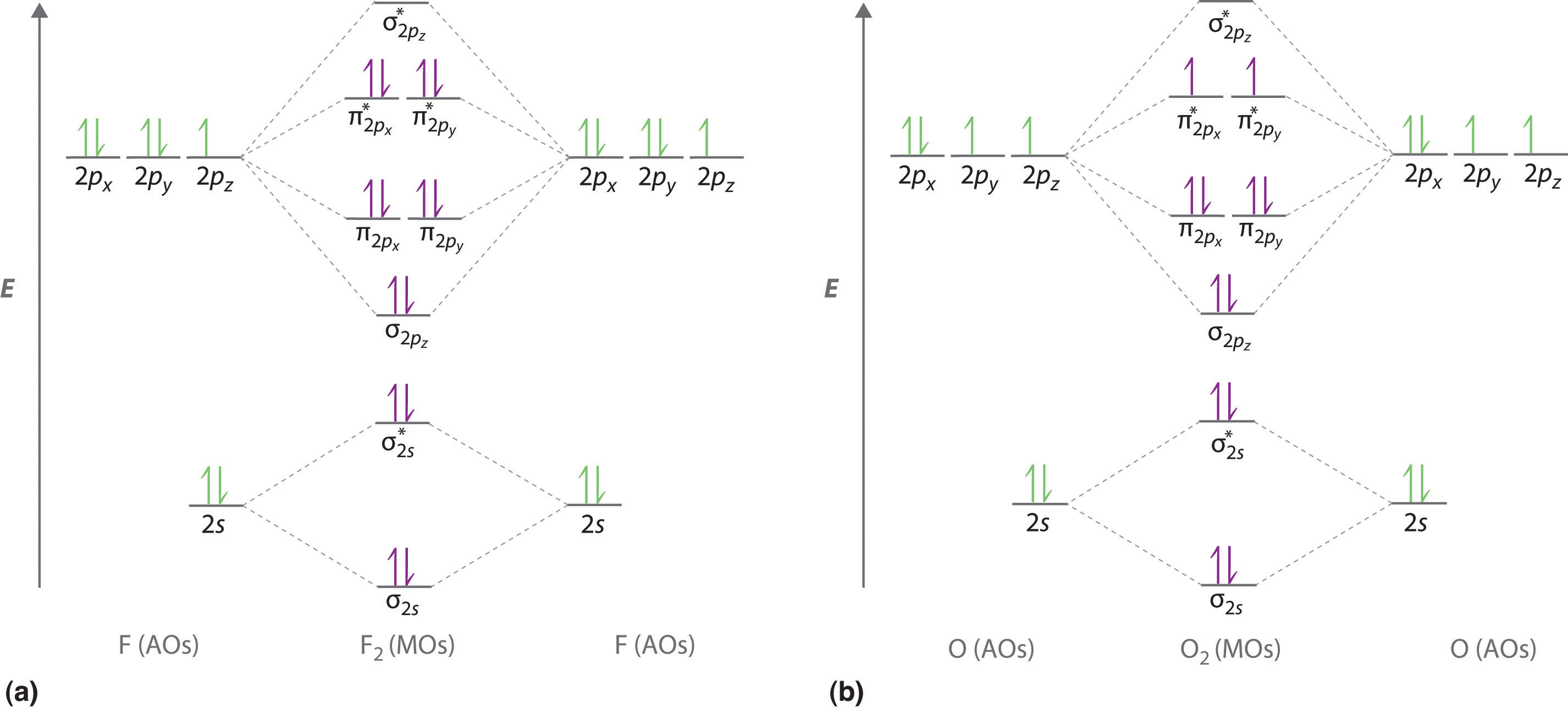
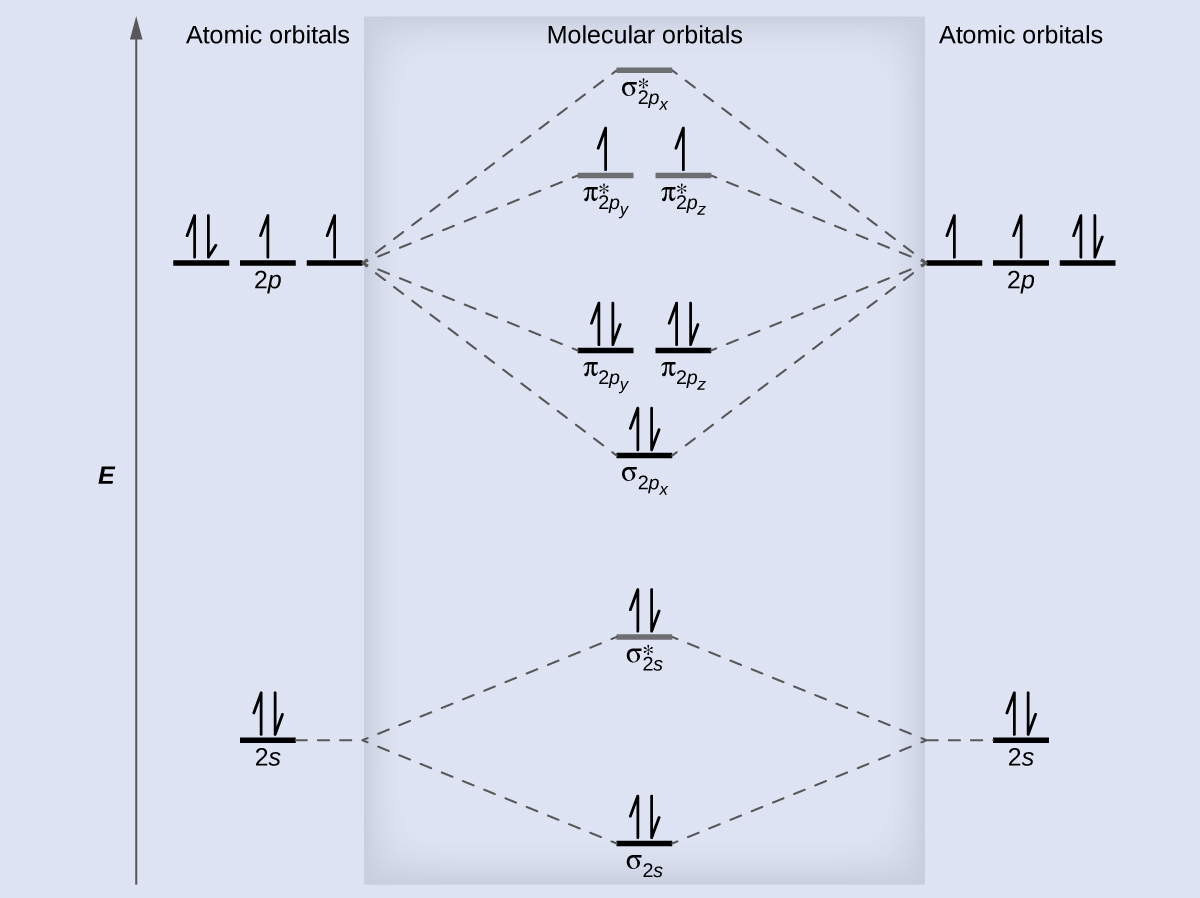
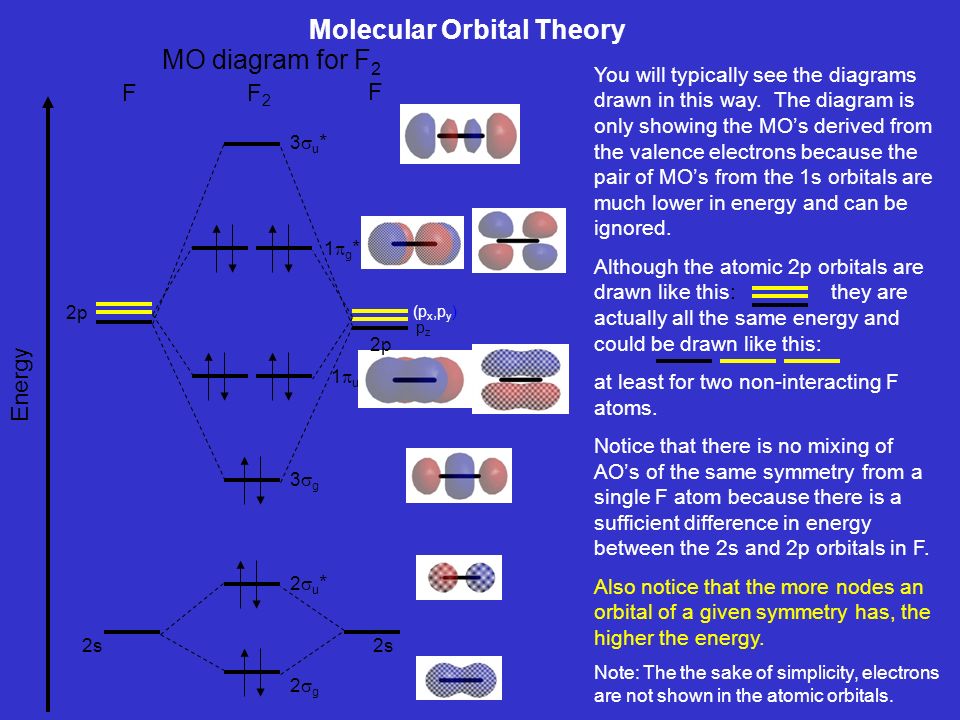
F2 molecular orbital diagram. 4 Lecture 2 Pi bond (π): bonding molecular orbital -The bonding electron density lies above and below, or in front and in back of the bonding axis, with no electron directly on the bonding axis, since 2p orbitals do not have any electron density at the nucleus. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... Here is a video that discusses over the Molecular Orbital Diagram for F2+ and F2+. Then compare their bond length, strength, bond order etc. And explaining a...
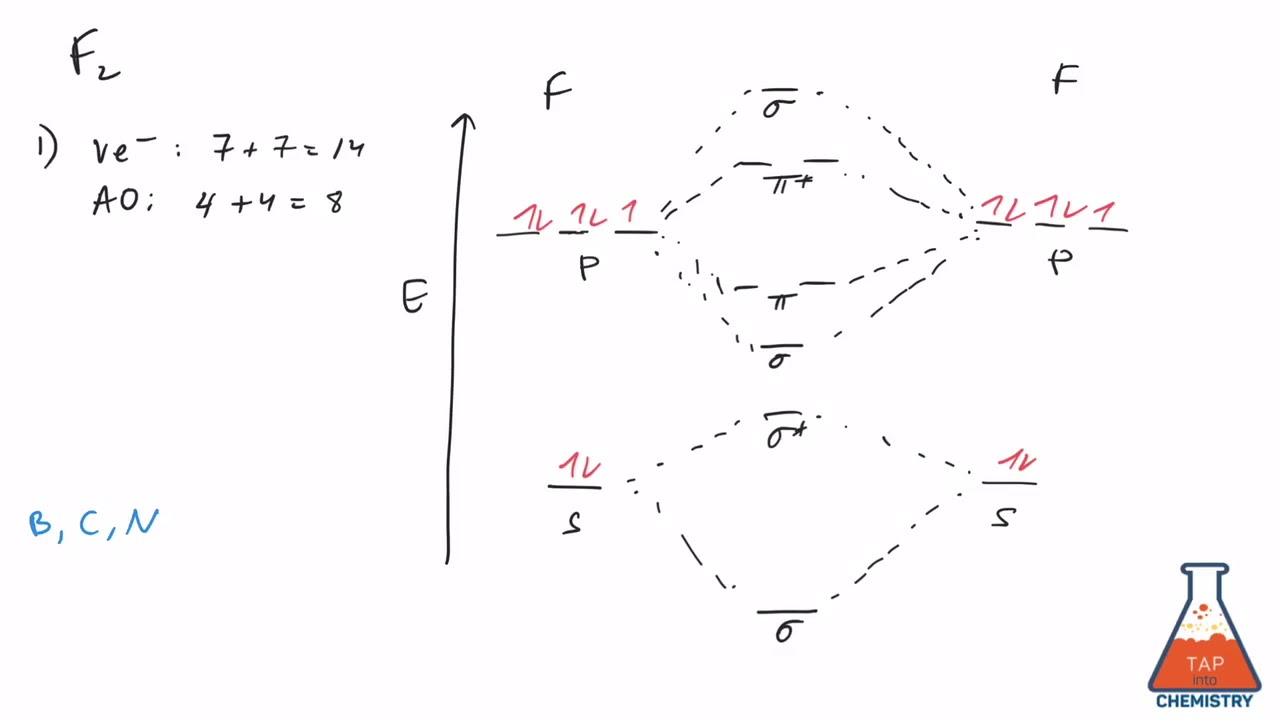
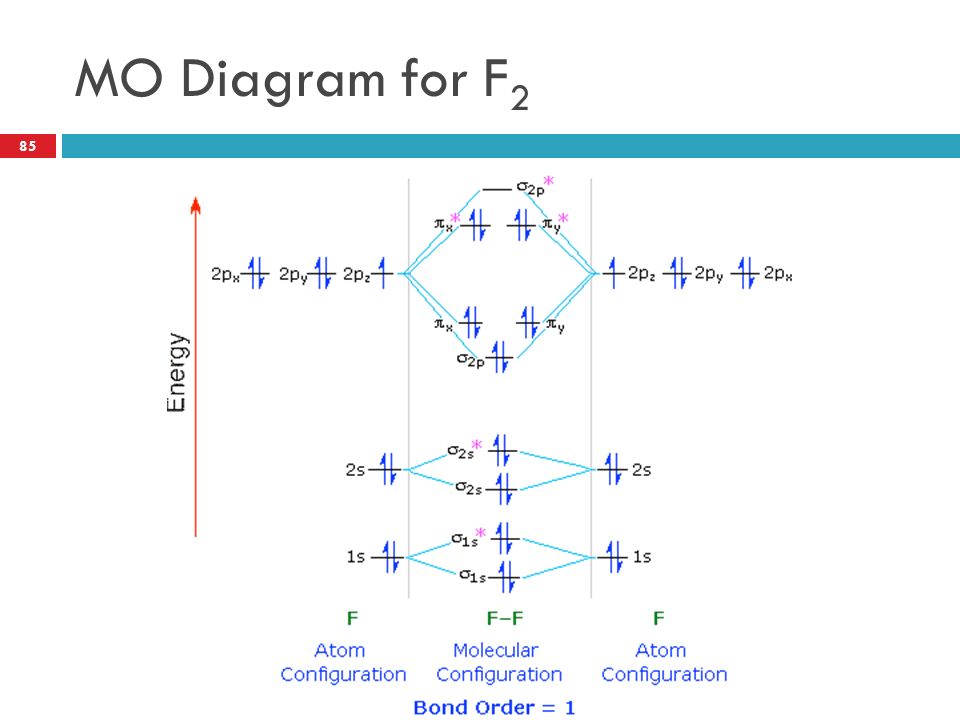
The bond lengths are inverse to the bond order, so the order is F2+ < F2 .There is 1 unpaired electron in F2+, 0 unpaired electrons in F2. Q12.14 Which of the following molecules have the shortest bond: F 2 ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram of \(Ne_2\) and \(Ne_2\). From that, describe the bonding scheme of those two molecules based on ... Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Page 1. MO Diagrams for Elements Li2 through Ne2. (Don't memorize.) Li2 through N2. O2 through Ne2. Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist.
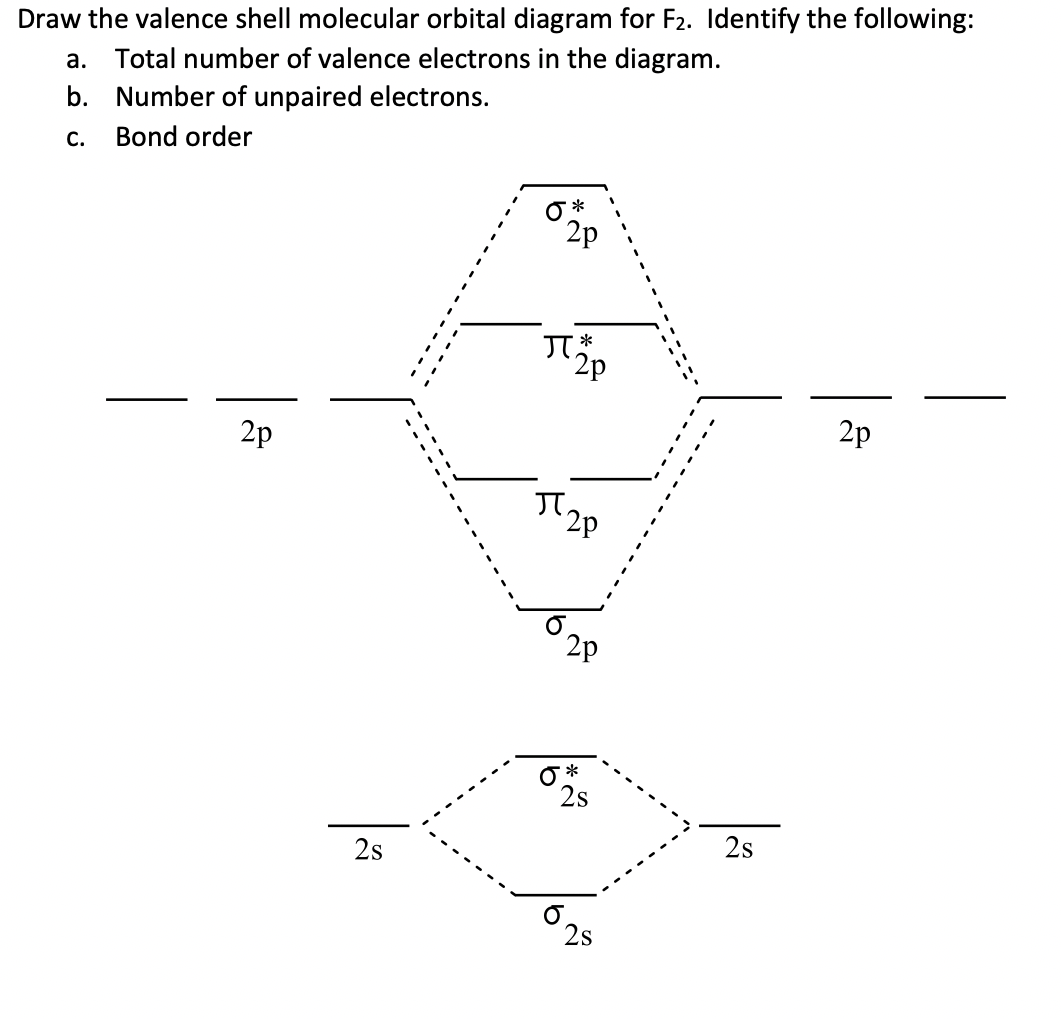
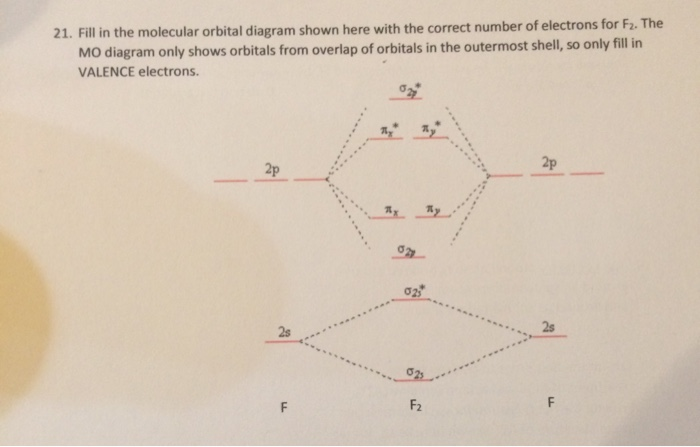
Below is the molecular orbital diagram for the fluorine molecule (F2) and images of several molecular orbitals that exist in this molecule. Fill the blanks below. Fatom F Fatom А ** tttt pfltit >pft t11 to f1 f1 att с D E F .t1 s stt 24 TL 1. a. The bond order for the F2 molecule is (enter a numeral). b. For example, an ns/ns overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this: and an np/np overlap for O2 and F2 gives: So, the full MO diagram is: Thus, the valence electron configuration is: (σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(π* 2px)2(π* 2py)2. Answer link. Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th... 15 F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. We assume that the electrons would fill the molecular orbitals of molecules like electrons fill atomic we will use this diagram to describe o2, f2, ne2, co, and no. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2p_ (sigma), so that is where the extra electron will be added.

Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Most Stable A Homeworklib
The two electrons in the p* 2p 2 orbitals have the same spin, and they are responsible for the paramagnetism of oxygen. As an exercise, please fill electrons in the molecular orbitals of a relative energy level diagram to derive and confirm the above conclusion as well as the conclusion regarding the \(\ce{F2}\) molecule.
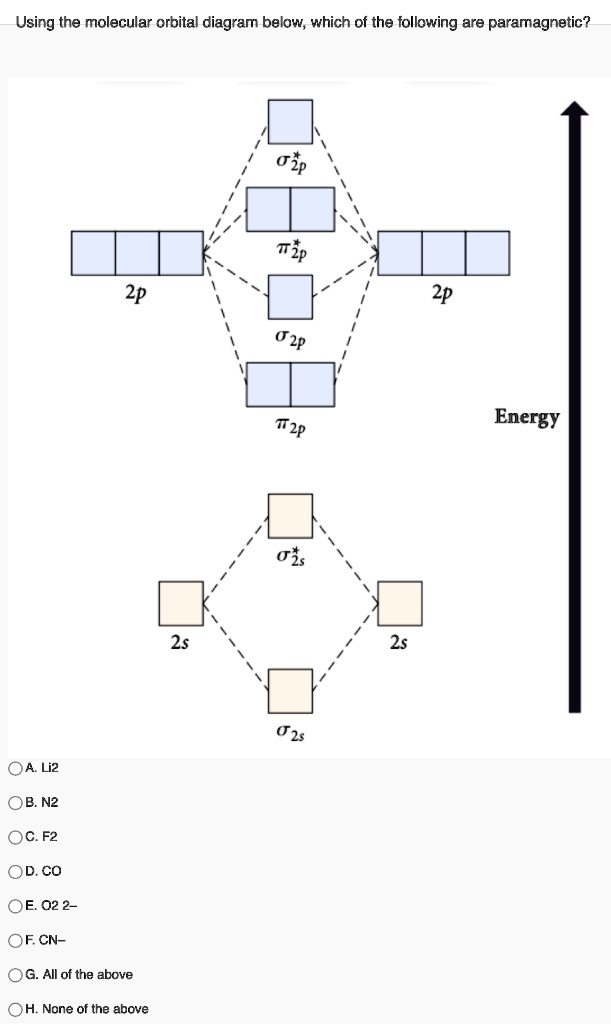
MO diagrams explain why some molecules exist and others do not. By looking at the O2 molecular orbital diagram, we can see that oxygen has BO of 2 because it has 10 bonding and 6 anti-bonding. Experiments show that each O2 molecule has two unpaired electrons. We can also notice the magnetic property of diamagnetic or paramagnetic.
mo bonding in f2 and o2 chemistry libretexts molecular orbitals mo are constructed from atomic orbitals in o 2 and f 2 there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials the relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals information from the mo diagram justify o2 s stability and show that it s bonding order is 2.
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. C would this ion exist. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with mo. For the ion f2.
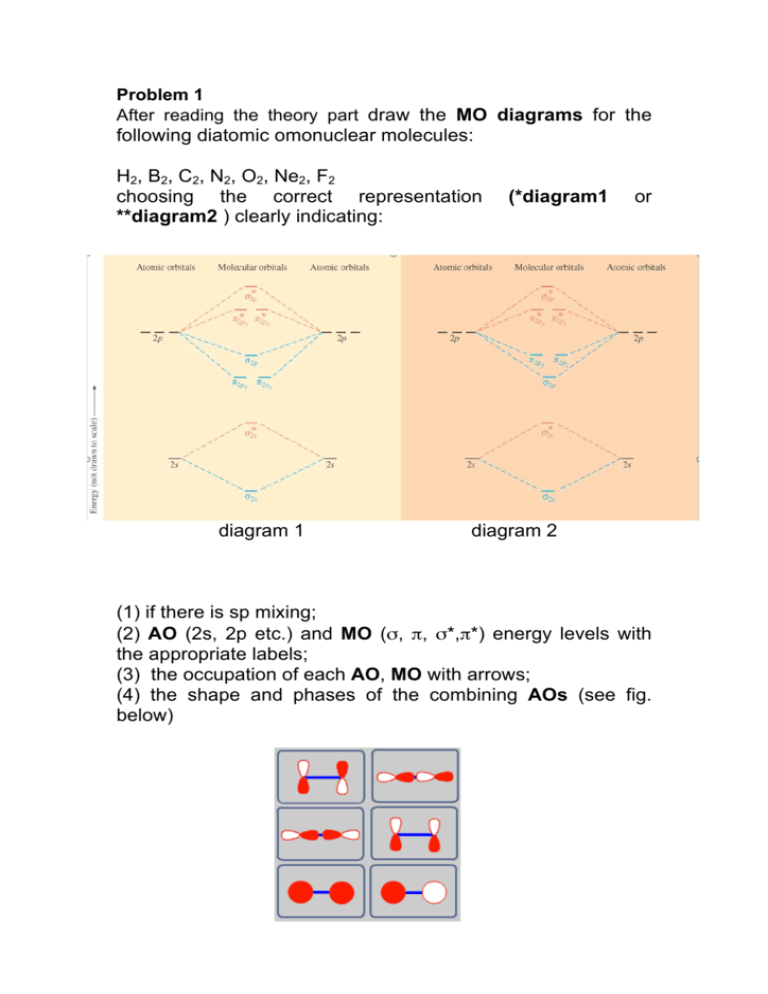
Molecular orbitals: Orbitals that span two or more atoms. These are constructed by overlapping atomic orbitals (AOs) which match in symmetry and size. In principle, To construct MO diagram of a any Molecule, first, set up Schrödinger wave equation for that molecule and then, solve it!!!
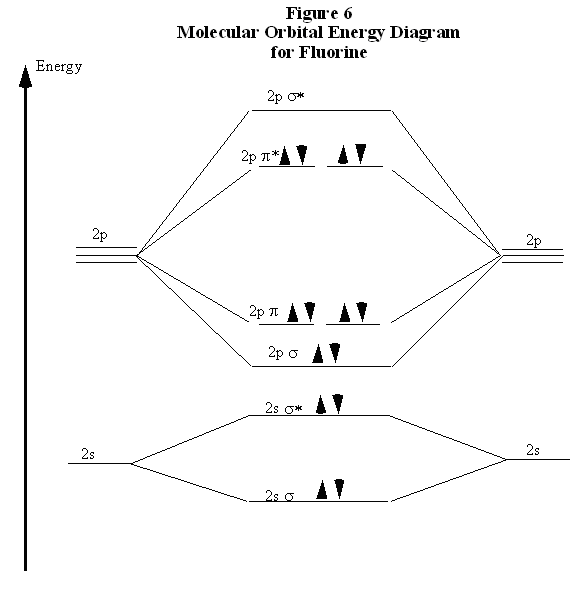
When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . ... B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. May 25, By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal 9 . It is ...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. Molecular orbital diagram for f2. The other molecular orbital produced s h h shows a decrease in electron density between the nuclei reaching a value of zero at the midpoint between the nuclei where there is a nodal plane.
The case of F2 is a simple one because of the symmetry and diatomicity of the molecule. In more complex molecules (polyatomic and asymmetric), the extent of mixing and thus the contribution of individual atomic orbitals to form a particular molecular orbital depends on the relative energy alignment of the atomic orbitals. F2 Polarity
Solved 5 Draw Complete Molecular Orbital Diagrams To Compare The Bonding In C2 F2 And Cf A What Is The Bond Order Of Each B Which Of The Thre Course Hero
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Solve Study Textbooks. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Chemistry >> Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure >> Molecular Orbital Theory >> 37. Draw molecular orbital ...
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d...
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
Ppt Chemistry 445 Lecture 4 Molecular Orbital Theory Of Diatomic Molecules Powerpoint Presentation Id 794473

Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram To Show That N 2 Would Be Expected To Have A Triple Bond F 2 A Single Bond And Ne 2 No Sarthaks Econnect Largest

Molecular Orbital Diagram White Atomic Orbital Molecular Orbital Theory Molecule Bond Order Electron Valence Electron Nitrogen Molecular Orbital Diagram Diagram Molecular Orbital Png Pngwing










Comments
Post a Comment